Seatrec Names Pentagon Alum Jason Stack to Advisory Board
Seatrec Names Pentagon Alum Jason Stack to Advisory Board
Extensive experience in developing and managing advanced autonomous naval and maritime systems will guide the commercialization and deployment of Seatec’s technology across the defense, research, and Blue Economy domains
VISTA, Calif. – WEBWIRE – Thursday, April 4, 2024. Seatrec, a renewable energy company that harvests energy from temperature differences in the environment, today announces the appointment of Jason Stack, Ph.D., an engineer and former Deputy Director of the Navy’s Unmanned Task Force at the Pentagon, to its advisory board.
“We’re rapidly commercializing autonomous systems powered by the ocean’s temperature differences for critical research and defense, as well as those that will help expand the Blue Economy,” points out Yi Chao, Ph.D., CEO and founder of Seatrec. “Jason’s unparalleled expertise gained from a distinguished career in the US Navy is a tremendous resource to help us accomplish our mission.”
Stack’s time at the Pentagon included multiple formal appointments within NATO including the US National Representative for Systems, Concepts, and Integration within the NATO Science & Technology Organization. Following his role at the Pentagon, he is co-founding a startup in the maritime space - still in stealth - and works as the company’s CTO.
He began his career designing and prototyping heavy equipment and industrial electronics at two manufacturing companies before earning his Ph.D. and moving to the Department of Defense (DoD). During his two-decade career at the DoD, Stack led programs at the Office of Naval Research (ONR) in maritime platform, sensor, perception, effector, and autonomy development. He then transitioned to an executive role where he acted as ONR’s Technical Director and served as director of the Ocean, Atmosphere, and Space Research Division before taking up his post at the Pentagon.
“Autonomous systems hold great potential for filling important capability gaps across a host of research, defense, and maritime missions but a reliance on batteries limits their endurance,” explains Stack. “Seatrec’s technology provides abundant power that is clean and sustainable to free those systems to reach their potential by providing robust function sets with near limitless endurance.”
Seatrec’s pioneering energy harvesting system uses phase change materials to harness energy from temperature differences between the ocean’s various depths. These materials contract and expand creating pressure that’s captured and converted into electricity. The clean, virtually limitless power enables scientists to integrate power-intensive sensors into its infiniTE™ float that were previously restricted by battery capabilities and lifespans.
Seatrec counts the US Navy’s Office of Naval Research among its early backers and in 2022 launched a project in partnership with the Naval Postgraduate School to integrate hydrophones into autonomous, ocean-going robots.
In 2023, the company was selected for the National Security Innovation Network (NSIN) Propel Hawai’i Accelerator. The program is a partnership between the NSIN and Decisive Point in collaboration with the U.S. Navy’s Pacific Fleet—the world’s largest fleet command encompassing 100 million square miles. Seatrec was selected from a competitive field of over 200 early-stage companies to join an elite cohort of enterprises developing cutting-edge technologies to help the modernization needs of the US Navy and the broader DoD community.
About Seatrec
Seatrec designs and manufactures energy harvesting systems that generate electricity from naturally occurring temperature differences in ocean waters. This renewable energy can be used to power deep water oceanographic research equipment such as floats, gliders, and autonomous underwater vehicles, resulting in the most scalable, cost-effective deep ocean data collection possible. Incorporated in 2016 by CEO, Dr. Yi Chao, Seatrec’s technology originated at NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology, to provide clean power for remote off-grid locations. The company is headquartered in Vista, CA. Visit us at www.seatrec.com and @seatrecinc.
Media Contact
Sean Yokomizo
Seatrec, Inc.
sean.yokomizo@seatrec.com
+1 925.878.1200
###
Seatrec Names Retired Rear Admiral John Neagley to Advisory Board
Seatrec Names Retired Rear Admiral John Neagley to Advisory Board
The 35-year veteran of the US Navy brings unique experience in leading organizations and teams in developing and operationalizing complex maritime technologies with particular focus on the Blue Economy
Seatrec, a renewable energy company that harvests energy from temperature differences in the environment, today announces the appointment of retired Rear Admiral and Founder/Principal of Blue Native Consulting, John Neagley, to its advisory board.
“John’s long and distinguished career in the Navy saw him successfully lead complex operations and the development of new technologies amid high stakes and high standards,” explains Yi Chao, Ph.D., CEO and founder of Seatrec. “His understanding of what it takes to succeed in a maritime environment and his passion for developing the Blue Economy is a perfect fit with our mission of providing clean, renewable energy to existing and novel applications.”
Neagley’s three-and-a-half decades of experience in the Navy saw him command a Navy Destroyer and serve on a number of surface combatants, including those that participated in Operations Iraqi Freedom, Enduring Freedom, and Desert Fox. Following his time at sea, Neagley managed a host of Naval research, development, and procurement projects, including acting as the executive officer for Littoral Combat Ships (PEO LCS). Before his retirement, he oversaw the Program Executive Office, Unmanned and Small Combatants (PEO USC) that set the course and scope of responsibilities for both manned and unmanned systems.
“The maritime environment is demanding and providing clean, renewable power to the most remote areas has always been a limiting factor,” points out Neagley. “Seatrec’s technology opens up exciting possibilities for maritime applications and for expanding the Blue Economy.”
Seatrec’s pioneering energy harvesting system uses phase change materials to harness energy from temperature differences between the ocean’s various depths. These materials contract and expand creating pressure that’s captured and converted into electricity. The clean, virtually limitless power enables scientists to integrate power-intensive sensors into its infiniTE™ float that typically require shore-supplied power or direct ship support via tethering.
The company counts the US Navy’s Office of Naval Research among its early backers and recently launched a project in partnership with the Naval Postgraduate School to study the impact of noise pollution on the ocean environments powered by Seatrec’s technology.
About Seatrec
Seatrec designs and manufactures energy harvesting systems that generate electricity from naturally occurring temperature differences in ocean waters. This renewable energy can be used to power deep water oceanographic research equipment such as floats, gliders, and autonomous underwater vehicles, resulting in the most scalable, cost-effective deep ocean data collection possible. Incorporated in 2016 by CEO, Dr. Yi Chao, Seatrec’s technology originated at NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology, to provide clean power for remote off-grid locations. The company is headquartered in Vista, CA. Visit us at www.seatrec.com and @seatrecinc.
Media Contact
Sean Yokomizo
Seatrec, Inc.
sean.yokomizo@seatrec.com
+1 925.878.1200
###
Seatrec Partners with Naval Postgraduate School to Study Ocean Soundscape
Seatrec and Naval Postgraduate School Launch a New Project to Study Ocean Soundscape and Chart Impact of Noise Pollution on Ocean Environment
Hydrophone-equipped autonomous float powered by the ocean’s temperature differences will listen for clues to help minimize the impact of human noise
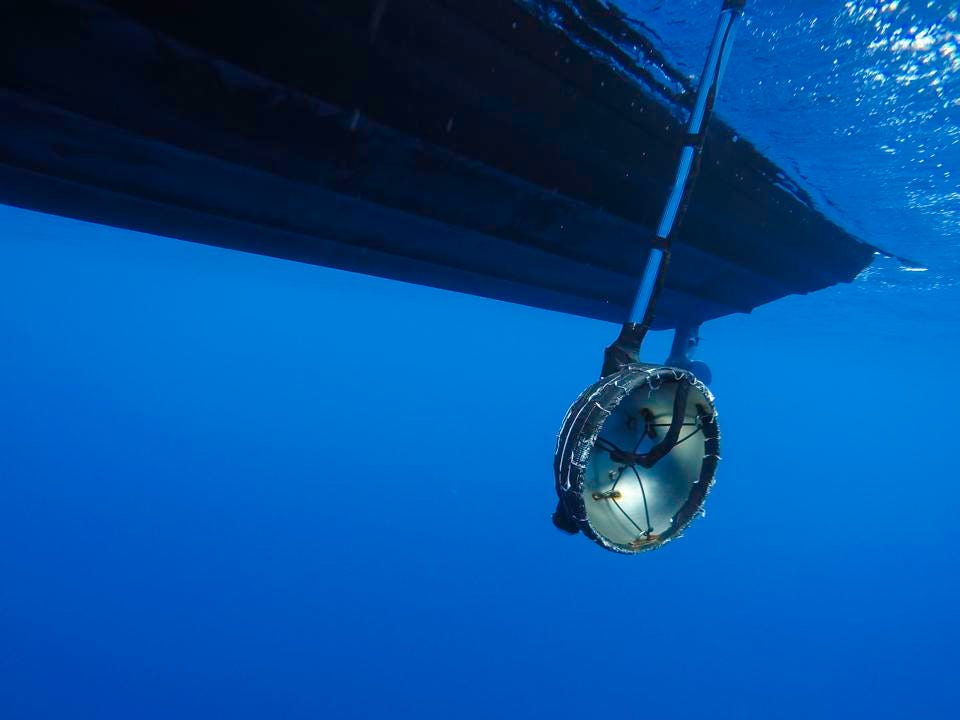
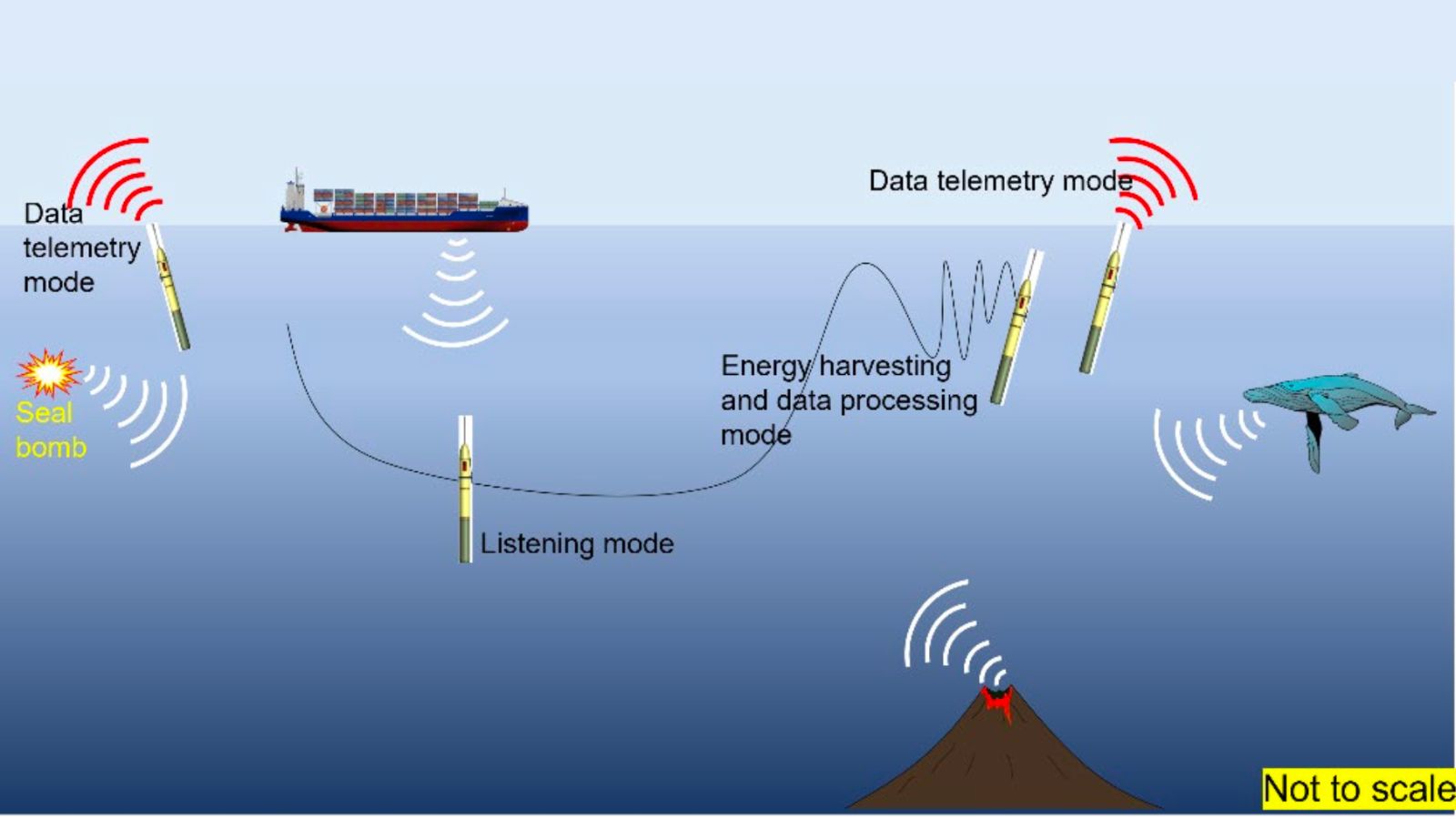
VISTA, Calif., November 14, 2022 - Seatrec and the Naval Postgraduate School (NPS) today launched a new project to study the impact of human-made noise on the ocean soundscape and marine life. An Ocean Sonics hydrophone installed on a Seatrec autonomous sustainably powered float system is the first of its kind and enables acoustic data to be collected anywhere in the world’s oceans nearly indefinitely.
“When it comes to understanding the ocean, sound is everything, but persistent listening is extremely difficult and expensive,” explains Yi Chao, Ph.D., Seatrec’s CEO and Founder. “The Naval Postgraduate School is a great partner, and we are excited to help them research acoustic impacts more effectively and affordably. Providing the necessary scientific instruments that are powered by the ocean’s own temperature differences opens the door to persistent monitoring of our oceans in an economical manner.”
Studies show that noise from humans adversely affects a broad range of organisms including whales, fish, jellyfish, squid and octopuses. High noise levels even contribute to deformities among scallop larvae. However, the true extent of impacts from noise pollution is not well understood.
The emergence of the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 brought with it unprecedented silence as human activities related to commerce and recreation all but ceased. That reduction in human activity gave scientists a new baseline for ocean noise and highlighted the impact that human noise pollution has on life in the ocean.
“Sound is the way the Navy and many marine animals ‘see’ through the ocean,” says John Joseph, the principal investigator and faculty associate for research at the Naval Postgraduate School. “It’s critical that we understand the reach and scale of the collective human impact on the ocean soundscape to inform strategies for protecting marine species and improving naval operations for the defense of our ships and Sailors at sea.”
The COVID-related silence also offered a powerful argument for broadening the deployment of hydrophones to monitor ocean noise and to include hydrophones on autonomous platforms to provide real-time acoustic data for the dynamic management of vulnerable areas. Underwater gliders have been used in this role and are also used by the Navy for passive surveillance, but they are powered by batteries with a limited lifetime and are usually confined to near the coast.
Traditional hydrophones are positioned at depths around 1,000 meters (3,300 feet), within the SOFAR (SOund Fixing And Ranging) channel, where the sound speed is minimum. Sound is trapped within this SOFAR channel by refraction and can travel slowly over great distances. Hydrophones can be lowered into the SOFAR channel from a ship, which is expensive to operate – often starting at $50,000 per day. They can also be placed on the seafloor and powered by fiber optic cables connected to a shore station on land, but there are only a handful of places with this infrastructure.
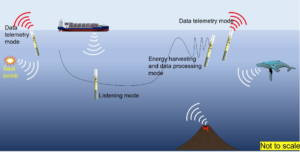 “Our hydrophone float powered by Seatrec’s patented energy harvesting system can be deployed into the SOFAR channel anywhere over the world’s ocean,” said Yi. “It offers nearly unlimited persistent surveillance of the ocean without the need for ship support as the float battery is recharged by the temperature differences in the ocean.”
“Our hydrophone float powered by Seatrec’s patented energy harvesting system can be deployed into the SOFAR channel anywhere over the world’s ocean,” said Yi. “It offers nearly unlimited persistent surveillance of the ocean without the need for ship support as the float battery is recharged by the temperature differences in the ocean.”
Naval forces have an inherent operational reason to be quiet at sea, and the research into ocean noise may provide additional insight for the Navy and Marine Corps in planning for future underway operations.
“Passive acoustic listening has many operational and research applications in the Navy, and our students at NPS conduct applied research to meet naval-unique needs for at-sea operations that require measurements of ambient noise, understanding soundscapes and monitoring of marine mammals,” added Joseph. “Because the Seatrec platform will be long-lived, and is remotely operated, it can provide extensive time series of information to oceanographers and naval researchers to measure acoustics and how they are changing from human impact including climate change.”
This research effort is supported by the Consortium for Robotics and Unmanned Systems Education and Research (CRUSER) at NPS, which is funded by the Office of Naval Research to provide a collaborative environment for the advancement of educational and research endeavors across the Navy and Marine Corps.
This project comes on the heels of Seatrec’s recent launch of Project NEMO – an initiative in partnership with The Nippon Foundation-GEBCO Seabed 2030 Project to install an active acoustic echosounder to Seatrec’s thermally powered float.
About Seatrec
Seatrec designs and manufactures energy harvesting systems that generate electricity from naturally occurring temperature differences in ocean waters. This renewable energy can be used to power deep water oceanographic research equipment such as autonomous profiling floats, resulting in the most scalable, cost-effective deep ocean data collection possible. The company is headquartered in Vista, CA. Visit us at www.seatrec.com and @seatrecinc.
About the Naval Postgraduate School
The Naval Postgraduate School is a defense-focused graduate university offering master’s and doctoral degrees in fields of study core to Naval-unique needs, the U.S. Armed Forces, DOD civilians and international partners. For information, visit: nps.edu.
Media Contact
Sean Yokomizo
sean.yokomizo@seatrec.com
+1 925.878.1200
Click here to read the full press release.
Seatrec Demonstrates Energy-Harvesting Solution for Ocean Instruments
Seatrec demonstrated that profiling instruments used for ocean exploration can be improved by pairing them with the SL1 thermal engine. A successful field trial was completed with Sea-Bird Scientific Navis autonomous profiling float mated to the Seatrec SL1. The SL1 harvests energy from temperature differentials in the ocean and converts it to stored electrical energy. Read more at Ocean News.